As we know there are four connecting types for the pipe fittings
- Socket Weld Fittings: Socket weld fittings involve inserting a pipe into a recessed area of the fitting and then filet welding it. This method provides a strong and permanent connection. Socket weld fittings are commonly used in smaller pipe sizes and applications where fluid flow needs to be controlled or redirected with ease.
- Butt Weld Fittings: Butt weld fittings are welded directly onto the pipe end to create a robust and leak-proof joint. This type of fitting is preferred in high-pressure and high-temperature applications where strength and integrity are crucial. Butt weld fittings are widely used in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemicals, and power generation.
- Threaded Fittings: Threaded fittings have external threads that screw onto the pipe, creating a secure connection. They are convenient for installations where disassembly and reassembly may be required for maintenance or modifications. Threaded fittings are common in plumbing systems, fire protection, and low-pressure applications.
- Flanged Fittings: Flanged fittings feature a raised surface (flange) with bolt holes around the perimeter. They are connected to the pipe by bolting together two flanged ends with a gasket in between to create a tight seal. Flanged fittings are suitable for applications requiring easy alignment, such as large-diameter pipes, and where frequent disassembly is necessary.
Socket weld fittings and butt weld fittings are popular choices for steel pipe fittings in pipeline projects due to their distinct installation methods and suitability for different operational requirements.
What is Socket Weld Pipe Fittings
Socket weld pipe fittings are designed with a recessed area into which the pipe is inserted, allowing for fillet-type seal welds to join them securely to valves, fittings, or flanges. They are favored for their robust structural strength and excellent leakage integrity, making them a preferred choice in pipeline projects where these attributes are crucial for performance and reliability.
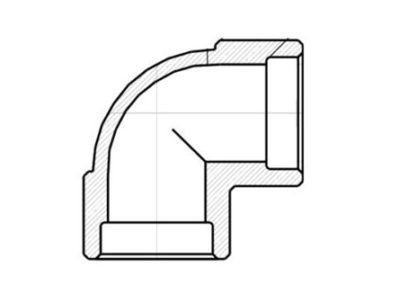
As below picture you can see the shape of 90 degree of socket weld elbow:
How to describe socket weld pipe fittings dimensions correctly
When describing socket weld pipe fittings dimensions accurately, it’s crucial to specify the outside diameter (OD) dimensions and the pressure ratings or thickness schedule required. Socket weld fittings are designated with pressure ratings such as class 3000, class 6000, and class 9000. These fittings are commonly referred to as SW pipe fittings, including SW elbows, SW tees, SW couplings, etc.Usage of socket weld fittings:
- Socket weld pipe fittings, such as elbows, tees, and reducers, are ideal for pipelines that handle toxic, flammable, or costly materials where leakage is unacceptable.
- They are compatible with ASME pipes, facilitating dimensional changes when needed.
- Designed for permanent installations due to their robust construction, ensuring excellent flow characteristics.
- Manufactured according to ASTM A234 standards and conforming to ASME B16.11, ensuring compliance with dimensions, pressure-temperature ratings, marking, tolerances, and material requirements for carbon steel and forged carbon fittings. These standards encompass bars, forgings, seamless tubes, and seamless pipes, ensuring adherence to chemical composition, mechanical properties, and manufacturing practices.
Socket weld pipe fittings types
Socket weld pipe fittings, akin to their butt weld counterparts, are crafted from a diverse array of materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, and alloy steel. These fittings find extensive utility across numerous industrial applications due to their robustness and versatility. Common types encompass socket weld elbows, tees, reducing tees for accommodating different pipe sizes, reducers for altering pipe diameters seamlessly, couplings for straightforward pipe connections, and socket weld flanges for attaching pipes to valves and equipment. These fittings are indispensable in sectors spanning from oil and gas to chemical processing, owing to their ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures while ensuring secure and efficient fluid flow within pipelines.Unit Weight in KG for SW fittings
| Nominal | Socket | Weld | Fittings | Weight | in KG | ||||||||||||||||
| Pipe Size | 45-Deg | Elbow | 90-Deg | Elbow | Tee | Cross | Coupling | Half | Coupling | Cap | |||||||||||
| 3000 | 6000 | 9000 | 3000 | 6000 | 9000 | 3000 | 6000 | 9000 | 3000 | 6000 | 9000 | 3000 | 6000 | 9000 | 3000 | 6000 | 9000 | 3000 | 6000 | 9000 | |
| 3/8 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.24 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.08 | ||||||
| 1/2 | 0.13 | 0.20 | 0.29 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.33 | 0.20 | 0.31 | 0.46 | 0.26 | 0.39 | 0.58 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.19 |
| 3/4 | 0.21 | 0.32 | 0.48 | 0.24 | 0.36 | 0.53 | 0.33 | 0.50 | 0.75 | 0.41 | 0.63 | 0.94 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.31 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.31 | 0.14 | 0,21 | 0.31 |
| 1 | 0.34 | 0,51 | 0.76 | 0.38 | 0,57 | 0.86 | 0.53 | 0.80 | 1.20 | 0,67 | 1.00 | 1.51 | 0.22 | 0.34 | 0.51 | 0.22 | 0.34 | 0.51 | 0.22 | 0.34 | 0.51 |
| 11/4 | 0.54 | 0.81 | 1.22 | 0.60 | 0.91 | 1.36 | 0.84 | 1.27 | 1.90 | 1.06 | 1.60 | 2.40 | 0.36 | 0.54 | 0.81 | 0.36 | 0.54 | 0.81 | 0.36 | 0.54 | 0.81 |
| 11/2 | 0.86 | 1.29 | 1.94 | 0.96 | 1.44 | 2.16 | 1.35 | 2.02 | 3.03 | 1.69 | 2.54 | 3.81 | 0.57 | 0.86 | 1.29 | 0.57 | 0.86 | 1.29 | 0.57 | 0.86 | 1.29 |
| 2 | 1.38 | 2.08 | 3.12 | 1.54 | 2.31 | 3.46 | 2.16 | 3.23 | 4.84 | 2.71 | 4.06 | 6.09 | 0.92 | 1.38 | 2.07 | 0,92 | 1.38 | 2.07 | 0.92 | 1.38 | 2.07 |
| 21/2 | 2.21 | 2.46 | 3.44 | 4.33 | |||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 3.53 | 3.93 | 5.50 | 6.92 | |||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 5.66 | 6.29 | 8.80 | 11.08 |
Socket weld Couplings
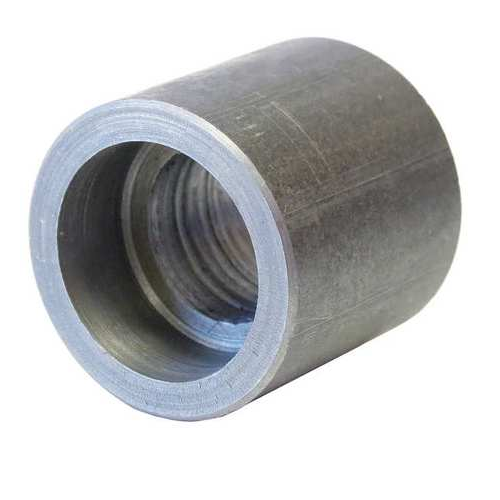
- Full-coupling
This pipe can join two pipes or to a nipple.
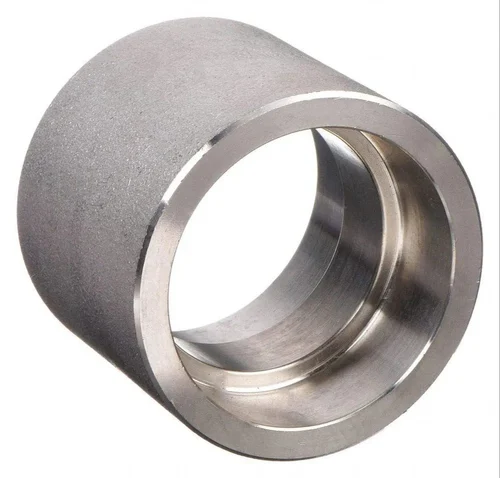

- Half-coupling
This can be directly welded to the run pipe in order to make a branch connection.

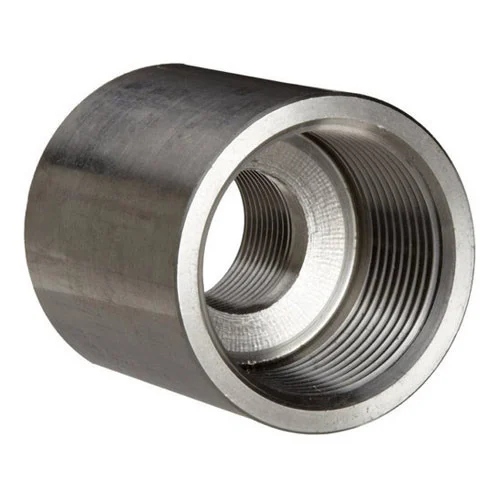
- Reducing coupling
It helps to join two different outside diameters of a pipe.

- Reducer insertThese have been manufactured according to MSS SP-79. It helps to enable economic and quick combinations of pipeline reductions. As such, these can be made by using standard socket weld fittings.
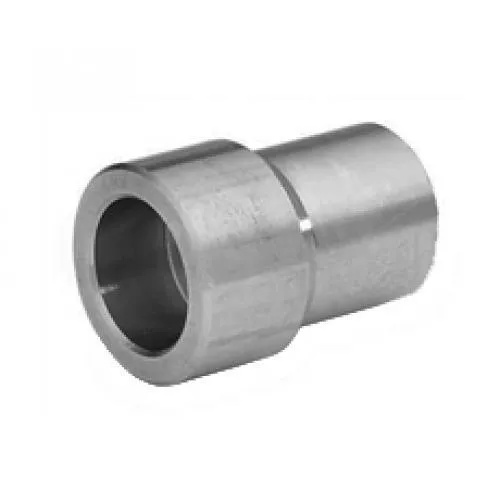

- Socket weld Union
A socket weld union is a screwed joint made of three interconnected pieces with two internal threads and a centerpiece. When the centerpiece is rotated, it draws the ends together. Tightly screwing the unions before welding is crucial to minimize seat warping and ensure a secure, leak-proof connection.

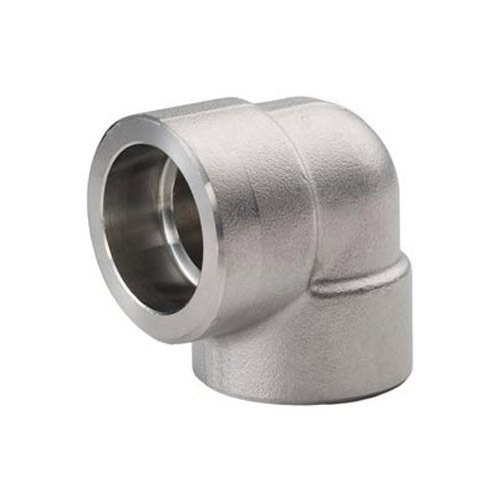
- Socket weld Elbow
Socket weld elbows, or SW elbows, are critical components in piping systems used to alter the direction of fluid flow. These fittings are primarily available in two angles: 45 degrees and 90 degrees. Forged during manufacturing, SW elbows come in both long radius (LR) and short radius (SR) versions. The LR model features a radius that is 1.5 times the outer diameter (OD) of the pipe, whereas the SR model has a radius equal to the OD. These elbows are vital for achieving smooth directional transitions in pipelines, ensuring efficient flow and minimizing turbulence.

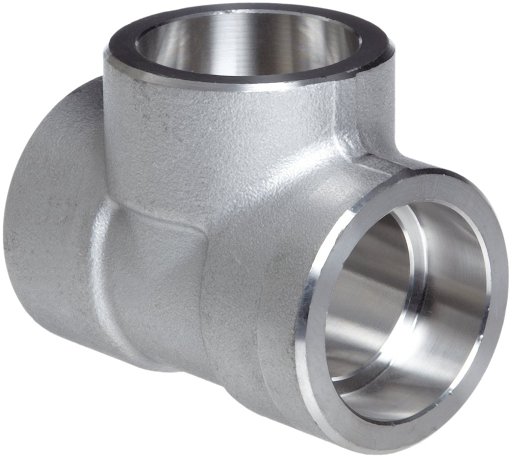
- Socket weld Tee (SW Tee)
Socket weld tees (SW Tees) are essential fittings in piping systems, designed to create branch connections. Straight tees have three openings of the same size, while reducing tees feature a smaller diameter branch, enabling a 90-degree branch off from the main pipe run. This smaller branch connects to a pipe of a reduced size, facilitating fluid distribution to different sections of the system. These fittings are critical for efficiently managing the flow in complex pipeline networks.

- Sockolet
A sockolet (derived from “socket” and “olet”) is a specialized type of socket weld pipe fitting. It is designed to connect a smaller diameter pipe to a larger diameter pipe, similar to a weldolet or threadolet. What makes sockolets unique is the internal socket feature within the olet, which provides a secure 90-degree connection. This design enhances the fitting’s strength, making it capable of handling high pressures.The bore of the sockolet aligns with the outlet bore, while the counter bore covers the outer diameter (OD) of the outlet. This configuration supports the pipe seated on the socket, ensuring a stable installation and robust welding strength. Sockolets are available in various pressure ratings, typically 3000#, 6000#, and 9000#, accommodating different industrial requirements.
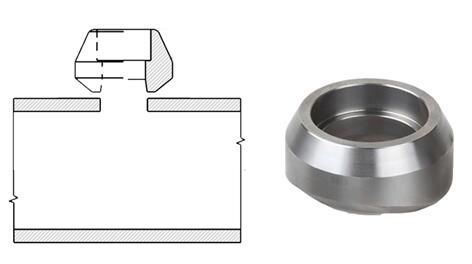
- Socket Weld Cross
Socket Weld Cross can also help to make a 90-degree branch from the main run of the pipe.

- socket weld cap
Socket weld cap is the end cap. It is used to seal the end of the pipe.
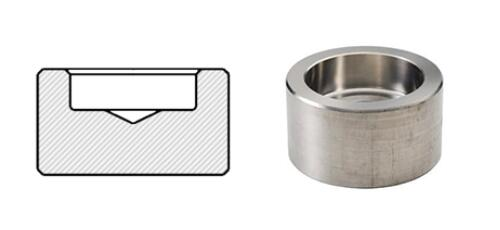
Socket Weld Flange Another SW Fitting
Socket weld flanges (SW flanges) are primarily used for smaller pipes that require high-pressure connections. These flanges have a distinctive design featuring a recessed shoulder on the inner bore. This shoulder ensures the pipe is correctly inserted, and then welding is performed to secure the connection between the pipes and flanges. This welding structure guarantees a smooth bore, promoting efficient liquid transmission within the pipelines.
SW flanges come in various types, including RF (Raised Face), FF (Flat Face), and RTJ (Ring Type Joint). They are available in multiple pressure ratings, classified as 150#, 300#, 600#, and up to 2500#, catering to a wide range of industrial applications.
Socket Weld Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
- Beveling Not Required: The pipe does not need to be beveled before welding, simplifying the preparation process.
- No Temporary Tack Welding: Proper alignment is ensured by the fitting principles, eliminating the need for temporary tack welding.
- No Bore Penetration: The weld metal cannot penetrate the bore of the pipe, maintaining internal integrity.
- Lower Construction Costs: Costs are lower compared to butt-welded joints, as there is no need for special machines or precise fit-up requirements.
Disadvantages
- Expansion Gap: The welder must ensure a 1.6mm expansion gap between the socket shoulder and the pipe, adding a layer of complexity.
- Corrosion Risk: Internal crevices and expansion gaps can promote corrosion, making socket welds less suitable for radioactive or corrosive environments.
- Unsuitable for Ultra High Pressure: These fittings are not ideal for ultra-high hydrostatic pressure applications, such as those in the food industry, due to the potential for crevices and gaps that are difficult to clean and can harbor contaminants.
Differences between socket weld and butt weld fittings
Socket weld (SW) fittings, as per ASME B16.11, allow pipes to be inserted into the fitting’s recessed area, requiring square cuts and minimal preparation. This simplifies installation and welding. Butt weld (BW) fittings, according to ASME B16.9, are welded onto pipe ends, matching pipe thickness and typically requiring beveled ends for a stronger connection.
Application differences between SW and BW fittings
Socket weld (SW) fittings are commonly utilized in smaller pipelines up to NPS 2 due to their ease of installation and sufficient strength for moderate pressure applications. They are ideal for systems where frequent disassembly is not required. In contrast, butt weld (BW) fittings are preferred for high-pressure and high-temperature pipelines, offering superior strength and integrity suitable for critical applications where welded joints must match or exceed base metal strength.
FAQs
What is a socket weld fitting?
A socket weld fitting is a type of pipe connection where the pipe is inserted into a recessed area of the fitting, valve, or flange. It’s joined by applying fillet-type seal welds to connect it to other sections of pipe or valves.
What rating are socket weld fittings?
Socket weld fittings are available in pressure ratings of 3000, 6000, and 9000 pounds per square inch (psi). These fittings conform to ANSI/ASME B16.11 standards and are suitable for various applications including elbows, couplings, reducers, tees, and crosses, with sizes typically up to 4 inches nominal diameter.
What is the strength of socket weld?
Socket weld joints typically exhibit approximately half the strength of butt weld joints. This makes socket welds suitable for small diameter pipelines (NPS 2 or smaller) where the lower strength requirement is acceptable. In contrast, butt welds offer superior strength and are preferred for high-pressure or high-temperature pipelines where robustness and reliability are critical.